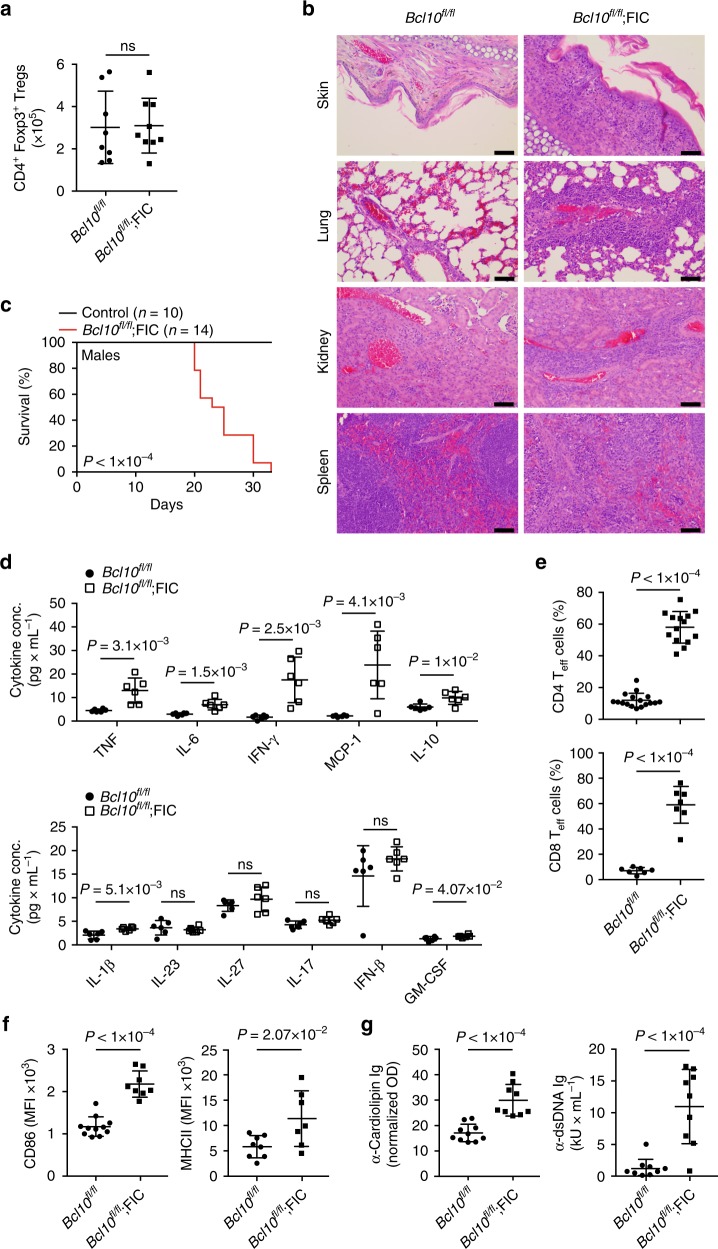
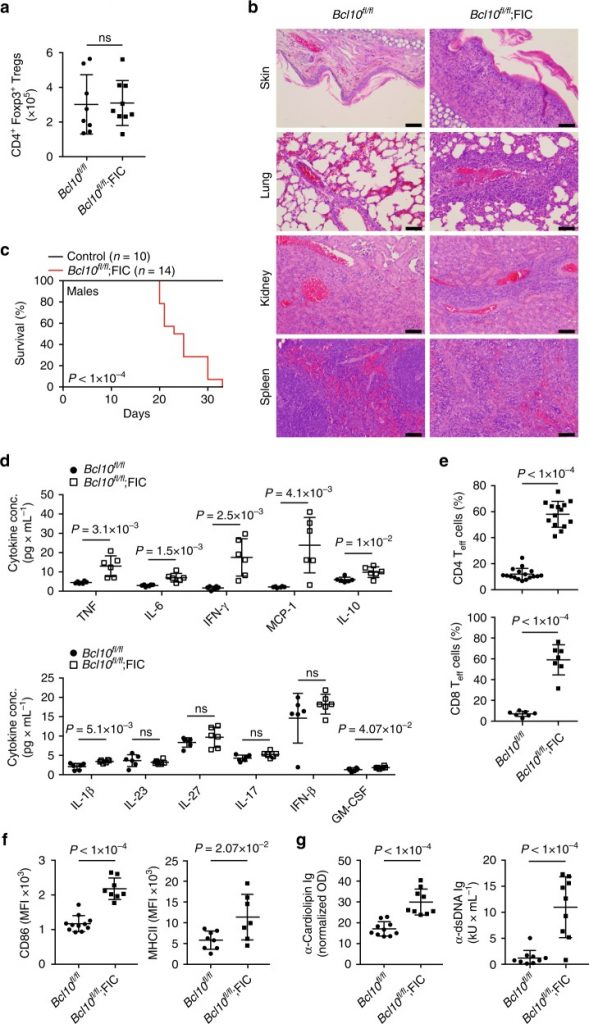
Bcl10-controlled Malt1 paracaspase activity is key for the immune suppressive function of regulatory T cells.
Regulatory T cells (Tregs) have important options in the inhibition of immune responses. Their development and suppressive options are managed by the T cell receptor (TCR), nevertheless the TCR signaling mechanisms that mediate these outcomes keep ill-defined.
Here we current that CARD11-BCL10-MALT1 (CBM) signaling mediates TCR-induced NF-κB activation in Tregs and controls the conversion of resting Tregs to effector Tregs under homeostatic conditions.
However, in inflammatory milieus, cytokines can bypass the CBM requirement for this differentiation step. By distinction, CBM signaling, in a MALT1 protease-dependent technique, is vital for mediating the suppressive function of Tregs.
In malignant melanoma fashions, acute genetic blockade of BCL10 signaling selectively in Tregs or pharmacological MALT1 inhibition enhances anti-tumor immune responses.
Together, our information uncover a segregation of Treg differentiation and suppressive function at the CBM superior diploma, and provide a rationale to find MALT1 inhibitors for most cancers immunotherapy.
BCL10 in cell survival after DNA hurt.
The superior safety mechanism of the DNA hurt response (DDR) developed by cells all through long-term evolution is an very important mechanism for sustaining the stability of the genome. Defects in the DDR pathway can lead to the incidence of diversified sicknesses, along with tumor development.
Most most cancers therapies set off DNA hurt and apoptosis. However, most cancers cells have the pure functionality to revive this hurt and inhibit apoptosis, in the finish leading to the development of drug resistance.
Therefore, investigating the mechanism of DNA hurt may contribute markedly to the future remedy of most cancers. The CARMA-BCL10-MALT1 (CBM) superior formed by B cell lymphoma/leukemia 10 (BCL10) regulates apoptosis by activating NF-κB signaling.
BCL10 is involved in the formation of complexes that antagonize apoptosis and contribute to cell survival after DNA hurt, with cytoplasmic BCL10 coming into the nucleus to promote DNA hurt restore, along with histone ubiquitination and the recruitment of homologous recombination (HR) restore elements.
This article evaluations the place of BCL10 in cell survival following DNA hurt.
By regulating miR-182-5p/BCL10/CYCS, sufentanil reduces the apoptosis of umbilical twine mesenchymal stem cells introduced on by ropivacaine.
Sufentanil is a form of opioid analgesic and is typically used to facilitate painless labor along with the native anesthetic ropivacaine.
One objective of the current analysis was to investigate the outcomes of sufentanil and ropivacaine on umbilical twine mesenchymal stem cells (UCMSCs). A second objective of this analysis was to seek out out whether or not or not sufentanil attenuated the cytotoxicity of ropivacaine in vitro.
UCMSCs have been divided into three groups: one was dealt with with ropivacaine at a spotlight of 50, 100, 200, or 400 μg/mL, one different was dealt with with sufentanil at a spotlight of 0.5, 5, 50, or 500 nmol/L, and a third was dealt with with a mix of ropivacaine at a spotlight of 200 μg/mL and sufentanil at a spotlight of 0.5, 5, 50, or 500 nmol/L.
Results indicated that cell proliferation decreased in cells dealt with with ropivacaine whereas it elevated in cells dealt with with sufentanil. In addition, sufentanil restricted the inhibitory influence of ropivacaine on UCMSC improvement in a dose- and time-dependent technique.
Combined remedy with ropivacaine at a spotlight of 200 μg/mL and sufentanil at a spotlight of 500 nmol/L decreased the proportion of ineffective and apoptotic UCMSCs, and fewer cells have been arrested in the S part as compared with cells dealt with with ropivacaine.
Sufentanil inhibited the apoptosis induced by ropivacaine by rising miR-182-5p, which regulated the expression of mRNA of the pro-apoptotic genes B-cell lymphoma/leukemia 10 (BCL10) and cytochrome c, somatic (CYCS). Sufentanil moreover elevated the expression of mRNA of anti-apoptotic genes. In transient, ropivacaine inhibits the cell viability and induces the apoptosis of UCMSCs in vitro whereas sufentanil attenuates this apoptosis by regulating miR182-5p/BCL10/CYCS.
